In this blog, we talk about the general idea about using and IDS or IPS. let’s recall that IDS/IPS stands for intrusion detection and prevention systems. We give examples of implementations of vendors and leaders of the market.
Scope of an IDS/IPS
Let’s start from a basic setup: clients that try to access ressources on hosted server via a network. what we may qualify as intrusion is by experience, by comparison to normal model of function, or some kind of probabiliy… and may concern the whole chain: hosts (operating system, file ressources, etc.) and network ressources
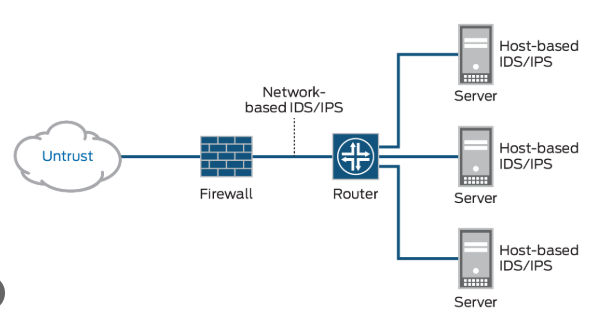
the figure shows a simple IDS/IPS deployment at hosts level (client and server) and network level (appliances in our case)
Different approaches
To qualify a system or network activity as an instrusion 3 main techniques are put into action: by exprience (sort of an intelligence), by normalization or by likeliness (kind of probability)
Intrusion detection by experience
Experiencing an intrusion is a way to model its behavior and systematically identify it. we talk about an intrusion signature kind of indentificator of an already identified intrusion activity. it is sufficient at IDS or IPS level to match patterns of the current traffic per example to the signature to state if the ativity is legitmate or not. we understand that the more the historical data is diverse and important the more the identification of threats is efficient
An intrusion is not a normal activity
In addition to information about intrusion that we gain by experience, we could choose another approach that is based on our deep understang of how our system and network ressources may be used normally. any change or deviation to this way of operation (or standard) should alarm on the possible violation of the security policy.
Give it a probability
Working by experiencing all the possible threats or qualifying the normal activity maybe very hard to achieve and would take a huge amount of ressources and time to be accurate. meanwhile working by a kind of probability based on some kind of likeliness to be or not to be subject to type of threat may be a rapid way to deploy IDS/IPS to overcome limitations of the other two approches
What to do next
The IDS and IPS systems in addition to be classified based on their scope (host or network) and approach (experience, normality and probability) could also be classified by the action they could have on the system or network. an IDS/IPS system may just alarm about a condition and give hand to another systems, or take effective action (block access, reroute traffic, etc.).
What implementation
Another criteria to choose an IDS/IPS system is its implementation: hardware, in clusters, as virtual machine, in the cloud… in path or out of path. because those systems integrate to the whole network, compatibility of function and operation with the other global network parts is required to keep the standard.
Being in path mean that the traffic get physically through the system, if the system is not available the network is down; on the other hand, when the system is out of path, the traffic flow is not affected in case of the system fails and other mechanisms are put into play to allow, reroute (bypass the system) or block the flow.
Market leaders network and host based systems
Network oriented systems
Related to the business research insights by 2023 the top ten of IDS and IPS companies are: Checkpoint, Cisco, Corero Network Security, Dell, Extreme Networks, HP, IBM, Juniper Networks, Mcafee and Nsfocus. they’re the leader of a market that is evaluated to 3.2 billion USD where the banking is more demanding (more than the half of the market share).
In the Checkpoint SG (Security Gateway) R70 the inspection is multilayered and framed as following: CoreXL/PSL (Packet Streaming Layer), IPS Unified Streaming, Protocol Analyzer (FTP), CMI (Protections and Context Matching), PM (first, second tier and accelerated paths), CMI final decision. In this processing, the flow is first parsed to the protocol to find out the corresponding context to which protections are available.
Host or system oriented systems
Concerning the host based IDS and IPS systems, a top 10 ranking is provided by Clear Network: AIDE, BluVector, Checkpoint Quantum, Cisco NGIPS, Fail2Ban, Fidelis Network, Hillstone Networks, Kismet, NSFocus, OpenWIPS-NG…
The AIDE kind of detection and prevention is very specialized to Linux systems (and MacOS) and to the integrity of the files.