This post is a part of series of posts about RIP dynamic routing protocol. Here we deepen our understanding on how RIP protocol advertises learnt RIP routes. A simple case is where a route is in the middle of this update process dans got a better route than RIP.
Introduction
Let’s recall first that RIP stands for Routing Information Protocol and it’s a mean by which routers in an autonomous domain exchange information about routes (how to reach destination representeds by those routes), dynamically without the need for doing it manually at each router. It is classified as distance vector which mean that its routing decision relies on a metric: if the first route has a better metric (small) it’s first considered for installation in the routing table. RIP is also an IGP, Interior Gateway Protocol, used within an autonomous system in contract with EGP that is used to connect two or more autonomous systems.
Test topology
Our test topology is a 3 routers network, emulated using Cisco IOS and GNS3, as shown the next figure:
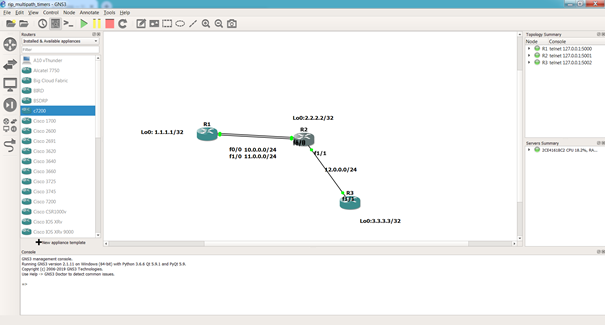
All routers : R1, R2 and R3 are configured for RIP operation: to advertise updates over and about all connected networks. Router R1 advertises 1.1.1.1/32 route into RIP domain. Router R3 receives 1.1.1.1/32 route information from R2 on the way from R3 to R1.
RIP into play
In this paragraph, let’s check how RIP manages routes advertisement and installations.
RIP database
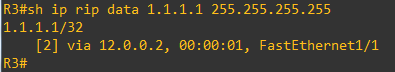
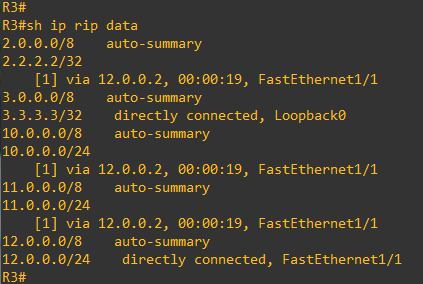
A show ip rip database “network” shows that R3 RIP process has learnt the route in its RIB (Rounting Information Base) indicating this information: the nexthop (R2 interface that has sent the RIP update) and outgoing interface on R3 (FastEthernet1/1) that points towards this nexthop. The route descriptor includes only one path descriptor.
Let’s observe that one route could have multiple paths attached to it…
This route gets next redistributed to the routing table, the default routing table in case of no VRF (Virtual Routing and Forwarding) or the GRT (Global Routing Table), that is effectively used by the router to perform the routing operation. The routing table accepts information from different routing sources: static and dynamic (IGP and EGP).
In the routing table
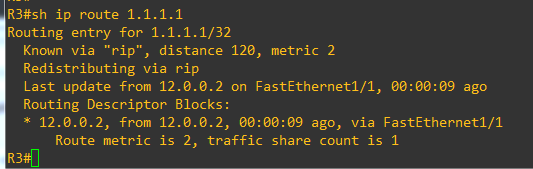
Using the command show ip route “network” we could get information about the existance of a specific route to this network, its origin (in our case RIP) and related admnistrative distance (120 in case of RIP, the more small the distance the most likely the route to be in the routing table), the last source of update and time, in addition to the routing descriptors blocks: nexthop, advertising gateway, outgoing interface, calculated metric from the perspective of the active router, traffic share count in situation of ECMP (Equal Cost Multiple Paths to the same destination)
But what if R2 installed another protocol or source to the same route (same subnet and mask) to R1 loopback0 network ? for test purposes, let’s configure at R2 level a static route that has a better administrative distance of 1 that RIP (120). As soon as the static route configured the previously RIP is no more in the default router routing table.
Let’s install a static route
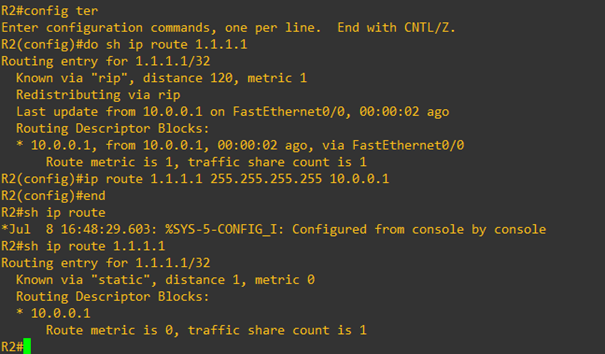
Let’s install a static route to see how RIP will react. We check in the routing table that the routing table is populated with the new static route.
The poisoning procedure into play
R2 starts poisoning the R1 route in its updates to R3. In the next figure, we show the output of the command debug ip rip in R3.
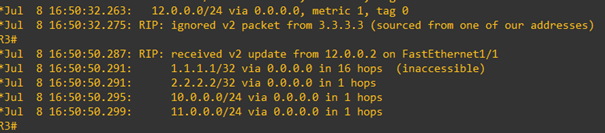
It says that R3 is receiving a v2 RIP update from R2 (12.0.0.2) on FastEthernet 1/1 with route 1.1.1.1/32 udpate set to inaccessible (equivalent to 16 hops far).
At R3 the route is also deleted from the RIP database and then, from routing main table (the route is no more being redistributed from RIP process to the default router routing table).
First conclusion and limitation
We conclude that for a RIP learnt route (using RIP updates) to be advertised downward (in our case from R2 to R3) it has to be in the routing table first. Because the router R2 has a better route to R1 network, the RIP adverstised route fails to enter the routing table and to be advertised to R3 by R2. This is very limiting because a simple static route in R2 is hidding the routes behind (on R1) from R3…
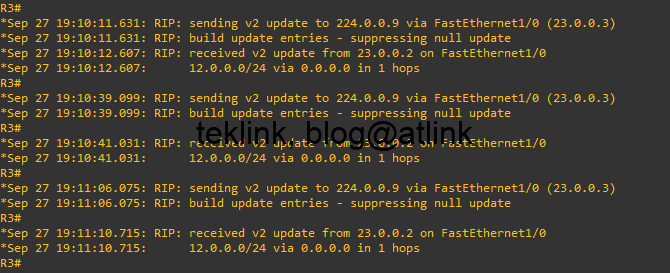
A show ip rip database, debug ip routing and debug ip rip on R3, show that no information about 1.1.1.1/32 R1 route is being received by RIP from R2.
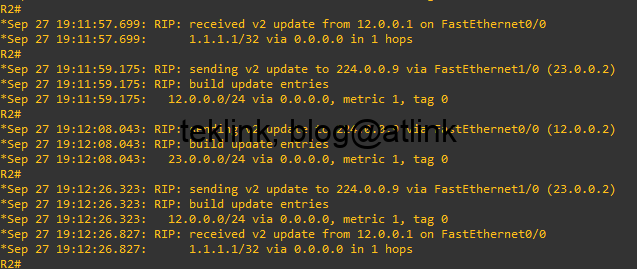
In R2, R1 route is being periodically advertised to R2 and does not do it to the RIP database neither to the default routing table. The fact that a better route (static route) exists in the routing table prevents also this route from being in the RIP database…
Further on
It is now interesting to find out if the route is not being advertised because of default routing table or the RIP database? also is it possible to have a route in RIP database that is not in the default routing table?
Conclusion
From this test, we could see that it is another caveat (or limitation) to see that the update about the R1 route is being sent to R2 evenif this latter does not use it, having no way to “prune” them at source!