Introduction and definitions
This post is a part of a serie of post about Multicast operation from the most basic setup to a much complicated one (scenario that include more routing and receiving options, etc.). We will explore the operation of SSM (Source Specific Multicast) in contrast with ASM (Any-source Multicast).
Let’s recall from previous parts, that IGMP is the procedure or protocol used by receivers (Multicast clients) to subscribe, to show their interest in a specific multicast…
IGMPv3 (RFC 4607) is an enchancement of IGMPv2 that allows the receivers to specify the source they wish in addition to the multicast group trafic. This is way we refer to this kind of multicast as SSM hinting on the fact that receivers try to receive the cast from a specific source (adding by this mean more control of this subscription).
By default, we use the 232.0.0.0/8 range for SSM
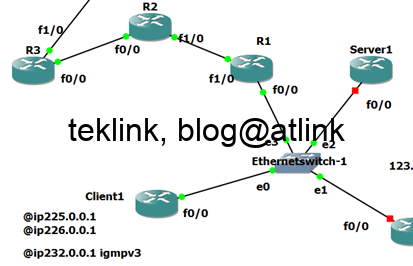
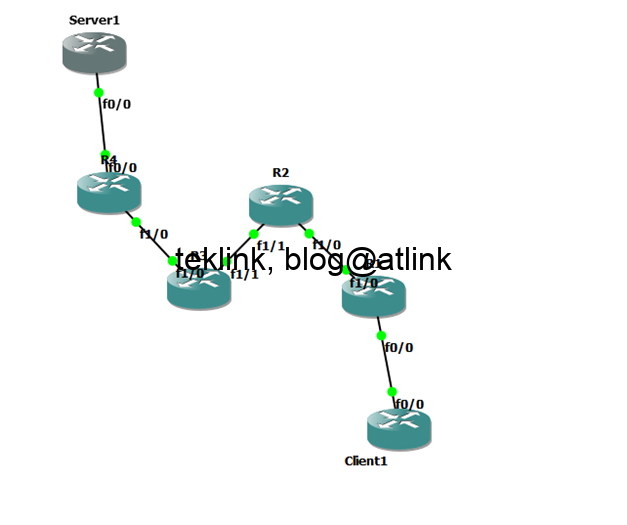
Lab setup presentation
In our lab setup

We configure Client1 to join SSM specific range @ip address 232.0.0.1 that is sourced from Server1 (in the same subnet)

A step-by-step
Without any other configuration (IGMP default to version 2 on This Cisco router). The IGMP membership record for the multicast group shows a small * to indicate any server (or sender), 2LA flags: version 2 of IGMP, Local and aggregate, and the interface joining the group (Fa0/0).


We see in the figure that Client1 is responding to multicast pings from Server1

and it is configured to join 232.0.0.1 from the wrong server address : @ip 123.1.1.254 of interface Fa0/0 (of the server); the correct @ip is indicated in the configuration of the interface Fa0/0 of the client using the command: ip igmp join-group source

as said before, Client1 records a version 2 IGMP group membership that is shown using the command: show ip igmp membership

the details of this record are given in the next output using the command: show ip igmp membership all.
the source information is included in the records

and the same if we configure the interface of IGMP version 3
Packet capture to confirm routers output (using CLI)
let’s check what happens on the wire, using wireshark a packet capture tool.
if IGMPv2, Client1 report includes only the group information…

in IGMPv3, Client1 sends a report including the source it wishes join

Test from a far away server (PIM routing)
We continue our test and multicast ping from Server1 (different from the configured source)
the pings succeed…
let’s try now from Server2

Without any configuration (only pim-dense mode, ASM multicast on R1, R2 and R3, RPF) the ping succeeds from Server2
the mroute tables
The mroute tables of routers R3 and the last hop router R1 show
at R3,

at R1,

Enable SSM
Let’s enable SSM multicast routing for this group by applying the “ip pim ssm” command on R1 in the global configuration mode (Cisco router)

debug IGMP
A “debug ip igmp” on R1 shows

R1 sends two membership report messages. The first message includes the multicast group and source addresses we want to receive. The second message includes the “mode”. There are two modes: 1 and 2.
The group record mode 2 for ssm group was ignored
mode 2?mode 2 (exclude): this is a list of source addresses that we refuse to accept multicast traffic from. Everything else should be forwarded.

The mode 1 from Client1 was accepted
mode 1? mode 1 (include): this is a list of source addresses that we accept multicast traffic from. Everything else should not be forwarded.
On R1 the IGMP table shows

an entry for reporter “Client1” that is flagged as version 3, M for SSM (S,G) and aggregate
an expiration timer is set for this entry also
Final mroute table
will the mroute table be populated?

yes but there’s somthing wrong with the outgoing interface list
the entry is flagged with a small s that indicate and SSM procedure
a debug on Client1 shows

reports are being sent
Check from the server perspective
Let’s check what happens from the server (Server2) perspective
The ping is no more accurate

at R2,

The (S,G) is correct
The flow is sent over the dense mode interface
Something wrong with R1 (RPF)
What’s wrong at R1?

The outgoing intreface list indicates Null and only Server1 source is present
A “debug ip mrouting” shows,

that the RPF information is incomplete (unknown)
debug RPF (Acceptance check failure)
A “debug ip mfib pak”, on the forwarding path, shows that

The flow destined for the group 232.0.0.1 and sourced from Server2 is being dropped due to Acceptance check failed…
Let’s clarify this point
What if I configured a source that is behind R1 (not on the same subnet)?

In R1, the mroute table shows

The entry passes the check because the source is not on the same subnet
And the incoming interface is put to what the ip routing table (unicast) returns

Let’s configure R1 to join this source on Server2
a debug on the Client1, shows that a new source has been created (12.1.1.254), a v3 report sent with this information on R1 subnet, etc.

Configuring mroute table
R1 adds now the mroute to the table

the P flag is suppressed and outgoing interface list updated with the correct information
What happen if I remove the static route to 12.1.1.254 subnet ?

A debug ip mrouting shows a triggered change of RPF to unknown
The ping responses stop and the mfib shows packets being dropped

We put back the route
Finally working setup
And multicast flows normally again

In summary,
the multicast ping works because the Client1 is configured to send a version 3 Igmp request of the group trafic from the specific source, SSM is enabled on R1 by mapping the default range to its operation (we could’ve mapped another range), and the source information is RPF checked…